Quick Start
If you don't have have access to the docker image or don't have access to the android sdk repository, please contact us at info@silencelaboratories.com.
Here is how you can setup the Mobile SDK and perform MPC operations in less than a minute.

You will create a working MPC two-party setup, where the first party, an Android application interacts with Duo Server as a second party. We are providing a demo server endpoint for your convenience.
Prerequisites
For quick testing, the demo server is already deployed at demo-server.silencelaboratories.com. We are using this server for the quickstart guide.
The Cloud Verifying Key for the demo server is 01829099948d222f9731323900bc42bd3cc6f4e692f920705a9959b3e52378f188.
The Cloud Node Endpoint for the demo server is demo-server.silencelaboratories.com.
Setup the Mobile SDK (Android)
Create a new Android Studio project by following the official guide or use existing one.
Dependency Installation
Step 1: Create access token for the repository
- Get access to the repository https://github.com/silence-laboratories/silentshard-artifacts from the Silence Laboratories team.
- Create a personal access token at https://github.com/settings/tokens with the following scopes
checked[✓] to access the repository, and it's
associated GithubPackages
through gradle.
- Under
repo-> [✓]public_repo - Under
write:packages-> [✓]read:packages
We can leavewrite:packagesuntouched/unchecked as we only need read access - It will end up looking like this : Two items checked everything else unchecked. See below.
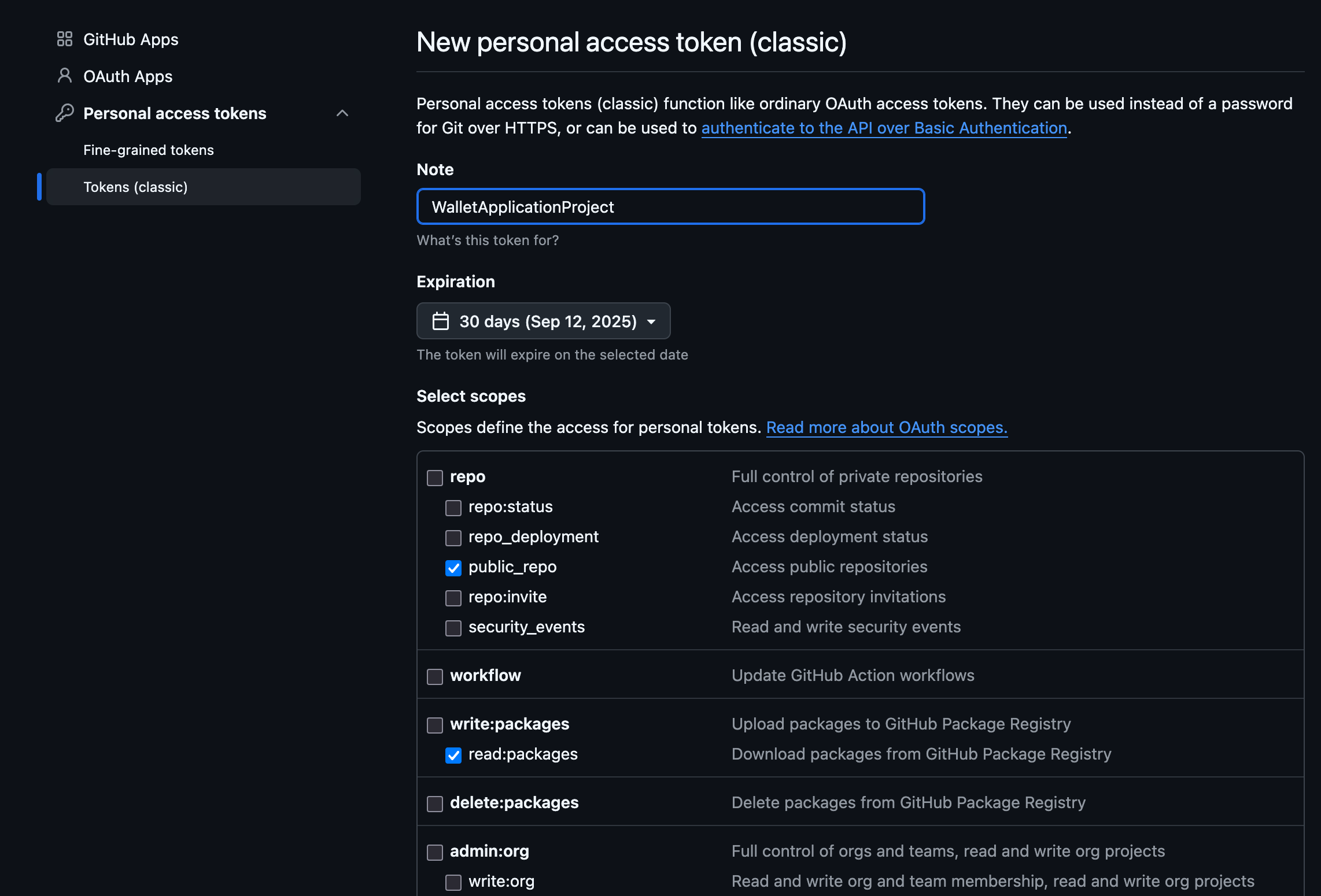
- Under
Step 2: Configure settings.gradle.kts
- Add the silentshard maven repo with the access credentials under the dependencyResolutionManagement -> repositories.
dependencyResolutionManagement {
repositoriesMode.set(RepositoriesMode.FAIL_ON_PROJECT_REPOS)
repositories {
google()
mavenCentral()
maven {
url =
uri("https://maven.pkg.github.com/silence-laboratories/silentshard-artifacts")
credentials {
// In production app we store private credentials outside of the files added to git.
username = "github_username"
password = "token_we_just_created"
}
}
//Other private repos or other resolution configuration. Or maybe another maven repo.
}
}
Step 3: Configure app level build.gradle.kts
- Add the silentshard dependency in your dependencies block
dependencies {
implementation("com.silencelaboratories.silentshard:duo-android:1.0.0")
//Your Other dependencies
//..
//..
}
Step 4: Gradle-Sync
- Sync gradle with project files.
Session Creation
Instantiate DuoSession object, which could be used to perform all of the supported MPC operations such as keygen, sign etc.
import com.silencelaboratories.silentshard.duo.SilentShard
import com.silencelaboratories.silentshard.duo.DuoSession
import com.silencelaboratories.network.websocket.WebsocketConfig
object Constants {
//Replace with your own
const val CLOUD_NODE_URI = "demo-server.silencelaboratories.com"
//Replace with your own
//const val PORT = "8080"
}
//Other party verifying-key/public-key. Replace with your own Verifying Key.
val cloudPublicKey = "01829099948d222f9731323900bc42bd3cc6f4e692f920705a9959b3e52378f188"
//Create websocketConfig to let SilentShard use default WebsocketClient.
val websocketConfig = SilentShard.buildWebsocketConfig {
withBaseUrl(CLOUD_NODE_URI)
//usingPort(PORT)
isSecureProtocol(false)
}
//Create storageClient instance to manage keyshare states
val storageClient = object : StorageClient<ReconcileStoreDao> {
/**
* Representing in-memory database. In real world it should be some SQL based DB or
* secure storage or custom hardware. It's up to the implementation app's use-case.
* */
private val keyshareDaoSet = mutableSetOf<ReconcileStoreDao>()
override suspend fun write(
dao: ReconcileStoreDao,
) {
if (!keyshareDaoSet.add(dao)) {
keyshareDaoSet.remove(dao)
keyshareDaoSet.add(dao)
}
}
override suspend fun read(
key: String,
): ReconcileStoreDao? {
return keyshareDaoSet.find { it.keyId == key }
}
}
//Create duoSession for EDSA algorithm
val duoSession: DuoSession = SilentShard.ECDSA.createDuoSession(
cloudPublicKey, websocketConfig, storageClient
)
//or for EdDSA algorithm
//val duoSession: DuoSession = SilentShard.EdDSA.createDuoSession(
// cloudPublicKey, websocketConfig, storageClient
//)
Run the MPC operations
After creating the session, you can perform MPC operations.
Key Generation
Generate MPC keyshares and return the client keyshare with keygen method.
// call this from a Dispatcher.IO coroutine
val result = duoSession.keygen()
result.onSuccess { keyshare ->
// Use the generated keyshare : ByteArray
Log.d("MPC", "Keyshare size: ${keyshare.size}")
}.onFailure { error ->
// Handle the error
Log.e("MPC", "Key generation failed: ${error.message}")
}
Signature Generation
Sign a message using the signature method.
val messageHash = "53c48e76b32d4fb862249a81f0fc95da2d3b16bf53771cc03fd512ef5d4e6ed9"
// call this from a Dispatcher.IO coroutine
val result = duoSession.signature(
keyshare = keyshare,
message = messageHash,
derivationPath = "m" // This is the default, use your desired path here. For e.g 'm/1/2'
)
result.onSuccess { signature ->
// Use the generated signature
Log.d("MPC", "Signature: ${signature.toHexString()}")
}.onFailure { error ->
// Handle the error
Log.e("MPC", "Signing failed: ${error.message}")
}
Complete Code Example
package com.silencelaboratories.silentshardduoquickstart
import android.os.Bundle
import android.util.Log
import androidx.activity.ComponentActivity
import androidx.activity.compose.setContent
import androidx.activity.enableEdgeToEdge
import androidx.compose.runtime.Composable
import androidx.compose.runtime.LaunchedEffect
import androidx.compose.ui.tooling.preview.Preview
import androidx.lifecycle.lifecycleScope
import kotlinx.coroutines.launch
import com.silencelaboratories.silentshard.duo.SilentShard
import com.silencelaboratories.silentshard.duo.DuoSession
import com.silencelaboratories.storage.StorageClient
import com.silencelaboratories.network.websocket.WebsocketConfig
import com.silencelaboratories.storage.silentshard.ReconcileStoreDao
class MainActivity : ComponentActivity() {
object Constants {
//Replace with your own
const val CLOUD_NODE_URI = "demo-server.silencelaboratories.com"
//Replace with your own
//const val PORT = "8080"
}
//Other party verifying-key/public-key. Replace with your own Verifying Key.
val cloudPublicKey = "01829099948d222f9731323900bc42bd3cc6f4e692f920705a9959b3e52378f188"
//Create websocketConfig to let SilentShard use default WebsocketClient.
val websocketConfig = SilentShard.buildWebsocketConfig {
withBaseUrl(CLOUD_NODE_URI)
//usingPort(PORT)
isSecureProtocol(false)
}
//Create storageClient instance to manage keyshare states
val storageClient = object : StorageClient<ReconcileStoreDao> {
/**
* Representing in-memory database. In real world it should be some SQL based DB or
* secure storage or custom hardware. It's up to the implementation app's use-case.
* */
private val keyshareDaoSet = mutableSetOf<ReconcileStoreDao>()
override suspend fun write(
dao: ReconcileStoreDao,
) {
if (!keyshareDaoSet.add(dao)) {
keyshareDaoSet.remove(dao)
keyshareDaoSet.add(dao)
}
}
override suspend fun read(
key: String,
): ReconcileStoreDao? {
return keyshareDaoSet.find { it.keyId == key }
}
}
//Create duoSession for EDSA algorithm
val duoSession: DuoSession = SilentShard.ECDSA.createDuoSession(
cloudPublicKey, websocketConfig, storageClient
)
//or for EdDSA algorithm
//val duoSession: DuoSession = SilentShard.EdDSA.createDuoSession(
// cloudPublicKey, websocketConfig, storageClient
//)
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
enableEdgeToEdge()
setContent {
val messageHash = "53c48e76b32d4fb862249a81f0fc95da2d3b16bf53771cc03fd512ef5d4e6ed9"
// call this from a Dispatcher.IO coroutine
LaunchedEffect(Unit) {
lifecycleScope.launch {
val result = duoSession.keygen()
result.onSuccess { keyshare ->
// Use the generated keyshare; Here using for signing
Log.d("MPC", "Keyshare size: ${keyshare.size}")
// call this from a Dispatcher.IO coroutine
val result = duoSession.signature(
keyshare = keyshare,
message = messageHash,
derivationPath = "m" // This is the default, use your desired path here. For e.g 'm/1/2'
)
result.onSuccess { signature ->
// Use the generated signature
Log.d("MPC", "Signature: ${signature.toHexString()}")
}.onFailure { error ->
// Handle the error
Log.e("MPC", "Signing failed: ${error.message}")
}
}.onFailure { error ->
// Handle the error˛
Log.e("MPC", "Key generation failed: ${error.message}")
}
}
}
}
}
}
Once the app launches, check your logcat logs to see the key generation and signing process updates in real-time.
Optional: Run your own Duo Server
Install Docker
- Linux
- macOS
- Windows
curl -fsSL https://get.docker.com | sh
Download and install Docker Desktop from the official website.
Alternatively, you can install using Homebrew:
brew install --cask docker
Download and install Docker Desktop from the official website.
Make sure to enable WSL 2 backend during installation for better performance.
Install OpenSSL
- Linux
- macOS
- Windows
# Ubuntu/Debian
sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get install openssl
OpenSSL is usually pre-installed on macOS. To install or update using Homebrew:
brew install openssl
Download and install from the official OpenSSL website.
Alternatively, you can install using Chocolatey:
choco install openssl
Or using Windows Package Manager:
winget install OpenSSL.OpenSSL
Login to Docker
- Login to docker using Personal Access Token(PAT) and your username.
Guide to generate GitHub Personal Access Token
- Go to GitHub Personal Access Tokens
- Click on "Generate new token", we are using the classic token for this guide.
- Enter a name for the token
- Select the "read::packages Download packages from GitHub Package Registry" scope.
- Generate the token.
Learn more about GitHub Personal Access Tokens here.
echo <PAT> | docker login ghcr.io -u <username> --password-stdin
Start the Server
For local setup, let's use this example docker-compose.yml
services:
duo-server:
image: ghcr.io/silence-laboratories/dkls23-rs/duo-server:v4
command: /usr/local/bin/sigpair-node
environment:
RUST_LOG: info
LISTEN: 0.0.0.0:8080
DEV_MASTER_SIGN_KEY: /run/secrets/duo-signing-master-key
FILE_STORAGE_URL: file:///data/
ports:
- 8080:8080
volumes:
- duo-server-data:/data
secrets:
- duo-signing-master-key
volumes:
duo-server-data:
secrets:
duo-signing-master-key:
file: ${MESSAGE_SIGNING_KEY:-./party_0_sk}
The docker compose file is configured to use the party_0_sk file in the root of the project. party_0_sk is the random bytes used as seed to create the server private key.
Create the party_0_sk file with random bytes in the root of the project.
openssl rand 32 > party_0_sk
Now let's start the server by running
docker compose up
If everything was setup correctly, the server should be running with these logs
Attaching to duo-server-1
duo-server-1 | WARN: The dotenv file is not set
duo-server-1 | 2025-09-16T09:59:09.200234Z INFO sigpair_node: Creating SimpleStorage
duo-server-1 | 2025-09-16T09:59:09.201975Z INFO sigpair_node: Party VK <YOUR_CLOUD_VERIFYING_KEY_HEX_STRING>
duo-server-1 | 2025-09-16T09:59:09.202413Z INFO sigpair_node: listening on 0.0.0.0:8080
Great! The server is now setup to perform MPC actions with our mobile.
In logs you will notice a hex string of length 66 (33 bytes). This is the YOUR_CLOUD_VERIFYING_KEY_HEX_STRING which will be used by server to verify the requests from other party (In this case, our mobile app).
The YOUR_CLOUD_NODE_ENDPOINT is the endpoint of the server. In this case, it is 0.0.0.0:8080 for ios and 10.0.2.2:8080 for android. Also you can use the IP address of your machine if you are running the server on your machine.
Second argument of the CloudWebSocketClient constructor is a boolean indicates if the connection is WSS or WS. Use true for secure connection, otherwise use false for local server.